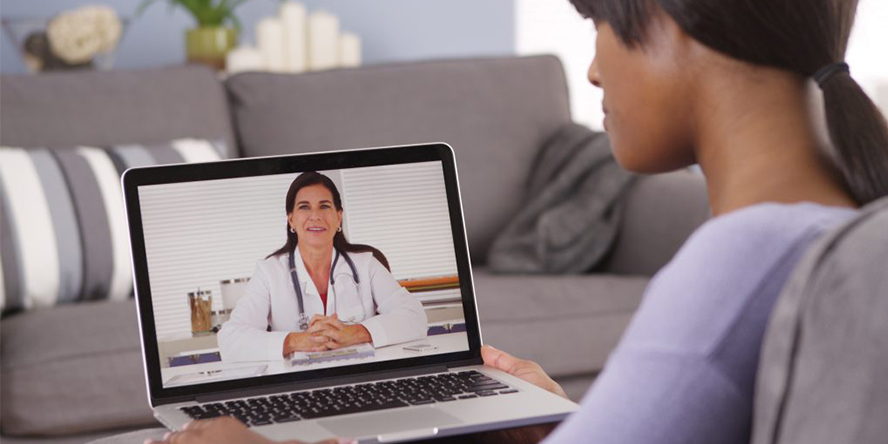
There have been many technological advances in the medical industries that have helped improve medical service. Everything from improved digital imaging options to electronic health records have impacted the way that doctors function to help give patients the best care. Telemedicine is one of these innovative new technologies that is poised to change the way that practices serve their customers in a way that no other technology has ever done.
Telemedicine involves the use of electronic communications and software to provide clinical services to patients without an in-person visit. Telemedicine technology is frequently used for follow-up visits, management of chronic conditions, medication management, specialist consultation and a host of other clinical services that can be provided remotely via secure video and audio connections.
Using telemedicine as an alternative to in-person visits has a host of benefits for patients and providers alike.
Patients enjoy:
- Less time away from work
- No travel expenses or time
- Less interference with child or elder care responsibilities
- Privacy
- No exposure to other potentially contagious patients
Providers enjoy:
- Improved office efficiency
- An answer to the competitive threat of retail health clinics and on-line only providers
- A better patient follow through and improved health outcomes
- Fewer missed appointments and cancellations
Despite the fact that virtual doctor’s visits are a relatively new phenomenon, awareness of, and comfort with, the option are increasing for both patients and physician practices. A recent study found that 74 percent of organizations were planning a telemedicine initiative within the next 12 months. Also, a separate study found that 74 percent of patients are comfortable communicating with doctors via technology.
History
What we recognize as telemedicine today started in the 1950’s when a few hospital systems and university medical centers started to try to find ways to share information and images via telephone. In one of the first successes, two health centers in Pennsylvania were able to transmit radiologic images over the phone.
In the early days, telemedicine was used mostly to connect doctors working with a patient in one location to specialists somewhere else. This was of great benefit to rural or hard to reach populations where specialists aren’t readily available. Throughout the next several decades, the equipment necessary to conduct remote visits remained expensive and complex, so the use of the approach, while growing, was limited.
The rise of the internet age brought with it profound changes for the practice of telemedicine. The proliferation of smart devices, capable of high-quality video transmission, opened up the possibility of delivering remote healthcare to patients in their homes, workplaces or assisted living facilities as an alternative to in-person visits for both primary and specialty care.
Uses
Telemedicine is making life easier for patients and doctors alike in a multitude of creative ways. Here’s a look at 10 ways that telemedicine technology is changing the delivery of healthcare.
1. Diagnose and Treat Strokes Faster
The sooner a stroke victim receives treatment, the better the chance of survival. In many cases, treatment hinges on the capability to identify key symptoms and administering medicine immediately. Unfortunately, emergency room physicians don’t always have the expertise to make these decisions, and small or rural hospitals don’t always have a neurologist on call.
2. Provide the ICU a Second Set of Eyes
Telemedicine technology is increasingly making its way into the intensive care unit. Telemedicine provides nurses and doctors a “second set of eyes” when they must treat several patients at once amid alarms and other distractions that may make them miss a medication dose, sudden change in blood pressure or other important signal.
3. Patient Rehab from Home
When patients are discharged, the care process is often just beginning. In many cases, patients find it difficult to travel to a health care facility regardless of whether they are in an urban or rural setting. The use telemedicine for rehab addresses these issues in several ways like conducting psychiatric assessments, leading therapy sessions, providing patients with online resources and remotely monitoring a patients’ pedometer readings to ensure that an exercise regimen is up to par.
4. Help Patients Reduce Their Risk of Heart Disease
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death around the world. Drug treatments or social/lifestyle changes can help prevent many cases. However, patients must work closely with their doctors to quit smoking, lose weight, change their diet or begin an exercise program, and making frequent office visits can be difficult for both parties. Telemedicine can be the answer. Researchers found that patients were nearly twice as likely to participate in cardiovascular disease management programs if they could send information to a healthcare provider online.
5. Diabetes Management
In the United States, healthcare costs related to diabetes are close to $100 billion a year. Research suggests that telemedicine improves the health of diabetics, especially older adults. This is because physician’s interactions with a patient boosts self-efficacy, or the belief that the patient can engage in activities that improve their condition and because telemedicine makes it easier for physicians to make treatment plans and set goals. Mobile health technology helps patients count calories, keep an eye on vital signs, log workouts and monitor medication doses and schedules.
6. Empower Patients to Manage Chronic Conditions
the concept of patient self-management using telemedicine can be applied to many long-term chronic medical conditions. Something as simple as routine three-minute phone calls with a health care provider will encourage patients to take blood pressure medication, refill prescriptions and remember their appointments. Patients can also describe symptoms to physicians, perform a number of self-tests and participate in step-by-step educational programs related to their particular disease.
7. Improve Oral Health
Telemedicine technology allows a doctor or dentist acquire medical images or other relevant data, assess it and send it to another physician for review. The main benefit of telemedicine in dentistry, then, is sharing records among dentists and dental specialists to determine if a certain procedure is necessary and, if so, how soon it must take place. Specialists can also help dentists spot problem areas and suggest preventive measures to a patient so that costly, complicated procedures can be avoided.
8. Link Patients to Dermatologists
Dermatology is a prime candidate for the use of telemedicine technology. Telemedicine can be used to show physicians certain skin related problems, and provide an easier way to make a diagnosis.
9. Provide Mental Health Consultations to Children
Traumatic events can have a dramatic effect on children, especially if they already suffer from mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety or hyperactivity. A study showed that the teleconferencing counseling sessions were the first consultations with a mental health professional for many students. Overall, nearly 70 percent of parents and guardians said the sessions helped their children perform better in school.
10. Improve Rural Healthcare Around the World
Telemedicine technology offers much promise for patients in the rural United States. Its biggest impact, though, may be felt parts of the developing world where healthcare services are equal parts scarce and inaccessible. Remote consultations can help address relatively minor conditions before they become major—treating cataracts before they cause blindness, for example, or ensuring that new mothers receive the educational resources they need to raise a child and take care of their own medical needs.
Today, telemedicine is used in medical fields such in many different ways to provide better care to communities underserved by physicians, hospitals or both; it is also considered a way to significantly reduce the cost of treating health conditions, including hypertension, diabetes and sleep apnea, which benefit from continued monitoring of a patient’s condition. Overall, telemedicine is changing the healthcare industry