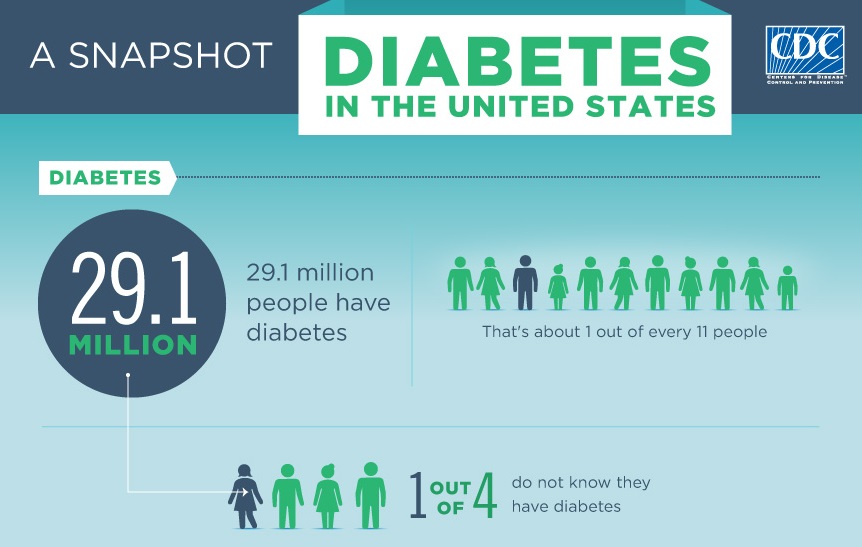
Did you know that 29.1 million people in the United States have diabetes? On top of that, an additional 8.1 million may be undiagnosed and unaware of their condition. About 1.4 million new cases of diabetes are diagnosed in United States every year. These number have grown a staggering amount within the past 20 years, making diabetes an extremely important National Health Concern. That is why November is designated as National Diabetes Awareness month by the federal government.
Diabetes can strike anyone, from any walk of life, and it often does. Worldwide, it afflicts more than 380 million people. And the World Health Organization estimates that by 2030, that number of people living with diabetes will more than double. To attempt to roll back this increasing numbers, we must actively try to stay away from diabetes prone activities. But before analyzing how to combat diabetes, we must fully understand what diabetes is.
To answer that, you first need to understand the role of insulin in your body. When you eat, your body turns food into sugars, or glucose. At that point, your pancreas is supposed to release insulin. Insulin serves as a “key” to open your cells, to allow the glucose to enter — and allow you to use the glucose for energy.
But with diabetes, this system does not work. Several major problems can occur that causes the onset of diabetes. The two most common forms of diabetes are Type 1 and Type 2. There are also other, less common, forms, such as gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy. Type 1 is the more severe form of diabetes, known as insulin-dependent diabetes. It is also sometimes referred to as “juvenile” diabetes, because it usually develops in children and teenagers, though it can develop at any age.
The most common form of diabetes is Type 2, or non-insulin dependent diabetes. Often called “adult onset” diabetes, Type 2 typically develops after age 35. However, a growing number of younger people are now developing type 2 diabetes. People with Type 2 are able to produce some of their own insulin, though often not enough. Sometimes, the insulin will try to serve as the “key” to open the body’s cells, allowing glucose to enter, but will not properly “open” the cells. This is called insulin resistance.
Treatment often focuses on diet and exercise. When blood sugar levels are still high, oral medications are used to help the body use its own insulin more efficiently. In some cases, insulin injections are necessary.
Often, Type 2 diabetes is tied to people who are overweight and live sedentary lifestyles, life aspects that can be changed. Before diabetes is diagnosed, there is a period where blood sugar levels are not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes, but are still higher than average. This is known as prediabetes. It’s estimated that up to 70% of people with prediabetes go on to develop Type 2 diabetes. Fortunately, progressing from prediabetes to diabetes isn’t inevitable. Although there are certain factors you can’t change — such as your genes, age, or past behaviors — there are many actions you can take now to reduce your risk of diabetes, and we have listed some of those actions below:
- Cut Sugars and Refined Carbs from your Diet
Eating foods high in refined carbs and sugar increases blood sugar and insulin levels, which may lead to diabetes over time. Avoiding these foods may help reduce your risk. - Exercise Regularly
Performing physical activity on a regular basis can increase insulin secretion and sensitivity, which may help prevent the progression from prediabetes to diabetes. - Drink water as your primary liquid
Drinking water instead of other beverages may help control blood sugar and insulin levels, thereby reducing the risk of diabetes. - Don’t smoke
Smoking is strongly linked to the risk of diabetes, especially in heavy smokers. Quitting has been shown to reduce this risk over time. - Create a Low Card diet
Following a ketogenic or very-low-carb diet can help keep blood sugar and insulin levels under control, which may protect against diabetes. - Avoid Sedentary Behaviors
Avoiding sedentary behaviors like excessive sitting has been shown to reduce your risk of getting diabetes. - Eat a High-Fiber Diet
Consuming a good fiber source at each meal can help prevent spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, which may help reduce your risk of developing diabetes. - Optimize Vitamin D Levels
Consuming foods high in vitamin D or taking supplements can help optimize vitamin D blood levels, which can reduce your risk of diabetes.
The bottom line is that you have control over many of the factors that influence diabetes. If you have viewing prediabetes or are at risk for developing diabetes, understand that you a not sentenced to a life with diabetes and can reduce your chances of fully developing the disease.
Eating the right foods and adopting other lifestyle behaviors that promote healthy blood sugar and insulin levels will give you the best chance at avoiding diabetes.





